Overview
In this blog post, we will discuss how to disable and enable indexes in SQL Server. Indexes are special data structures associated with tables or views that help speed up the query.
SQL Server provides two types of indexes: clustered index and non-clustered index. While indexes can improve query performance, they can also affect insert, update, and delete operations.
As a result, it is important to know how to disable and enable indexes as needed.
Syntax
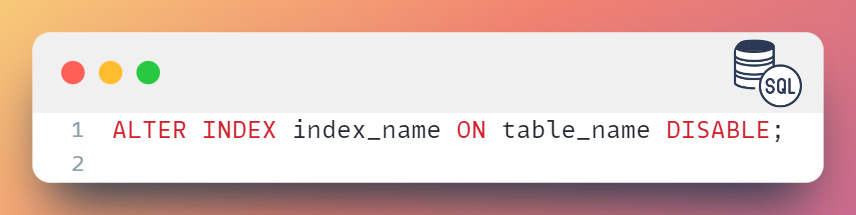
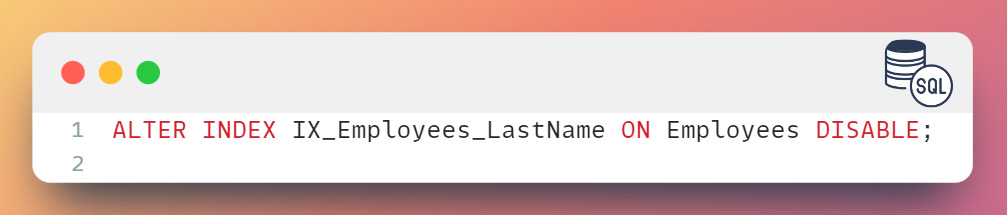
To disable an index, you can use the ALTER INDEX statement as follows:
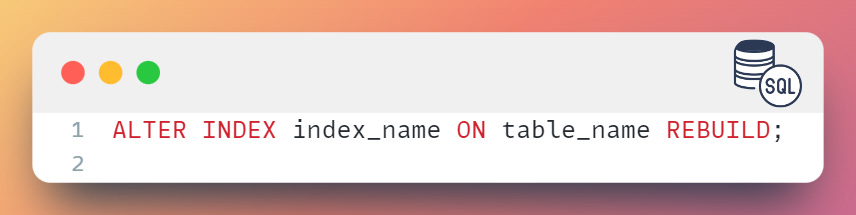
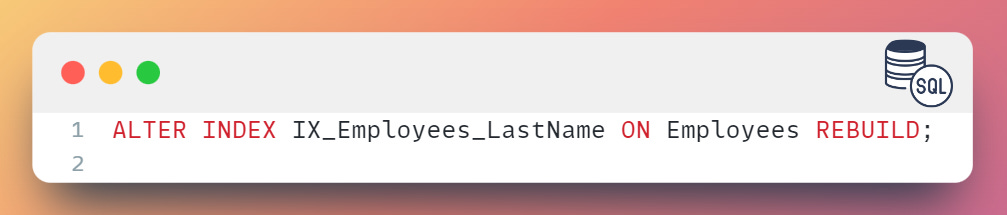
To enable an index, you can use the ALTER INDEX statement as follows:
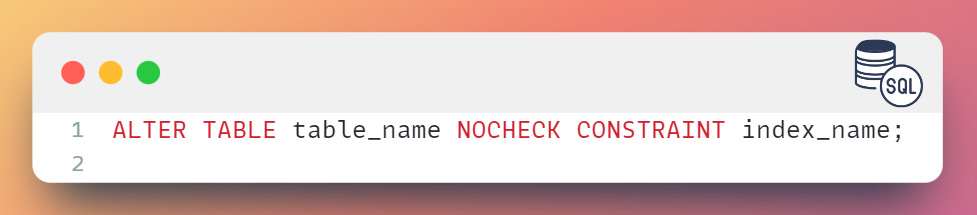
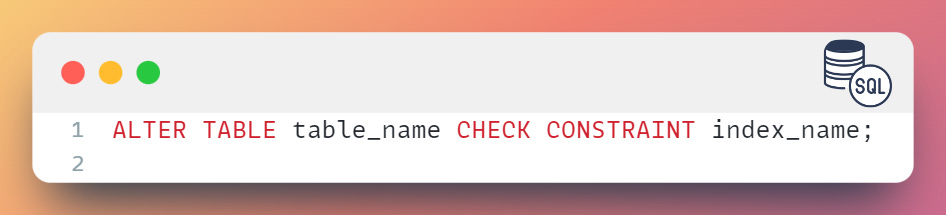
Alternatively, you can use the ALTER TABLE statement to disable and enable indexes as follows:
To disable an index:
To enable an index:
Examples
Here are some examples of using the ALTER INDEX and ALTER TABLE statements to disable and enable indexes in SQL Server:
To disable the IX_Employees_LastName index on the Employees table:
To enable the IX_Employees_LastName index on the Employees table:
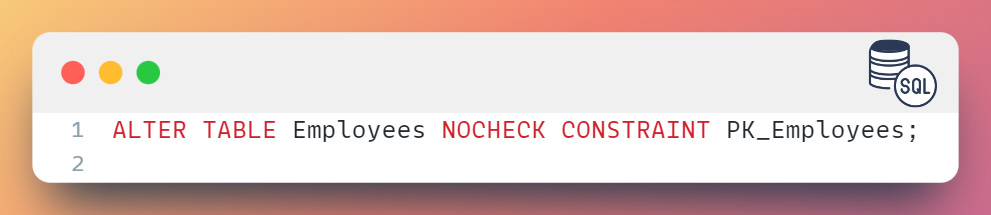
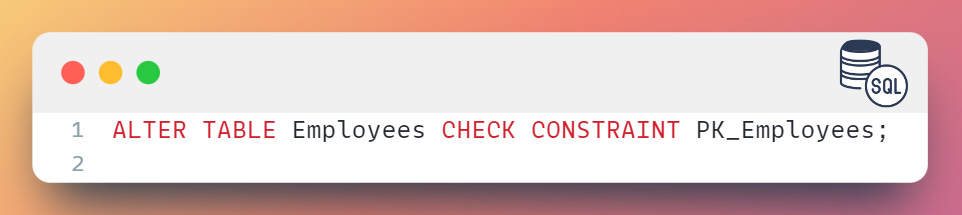
To disable the PK_Employees index on the Employees table:
To enable the PK_Employees index on the Employees table:
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
Disabling and enabling indexes can help improve the performance of insert, update, and delete operations by reducing index maintenance overhead.
Disabling and enabling indexes can also help improve the performance of queries by allowing the optimizer to choose a different index for a specific query.
Disadvantages
Disabling and enabling indexes can negatively impact the performance of queries that rely on those indexes.
Disabling and enabling indexes can also cause the optimizer to choose a less efficient execution plan for a specific query.
Use Cases
When you need to insert a large amount of data into a table, you can disable the indexes temporarily to speed up the insertion process. After the data is inserted, you can enable the indexes again.
When you are doing a data migration, you may need to disable the indexes first, and then enable them after the data migration is completed. This will prevent the indexes from being updated while the data migration is in progress, which can improve the performance.
When you are performing maintenance tasks on a table, such as rebuilding the indexes or reorganizing the data, you may need to disable the indexes temporarily to prevent any interference with the maintenance process.
Best Practices
Always enable the indexes after you are done with the tasks that required them to be disabled.
If you are disabling the indexes for a long period of time, consider rebuilding the indexes after you enable them again to ensure that they are optimized for the current data.
Avoid disabling the indexes unnecessarily, as it can negatively impact the performance of the queries that rely on those indexes.
If you need to disable multiple indexes at the same time, use the
DISABLE INDEX ALLstatement to disable all indexes on the table in one go, rather than disabling them one by one.Use the
ENABLE INDEXstatement to enable specific indexes, rather than using theENABLE INDEX ALLstatement, to avoid enabling any unnecessary indexes.
Summary
In this blog post, we learned how to disable and enable indexes in a SQL Server database.
We also discussed the use cases and best practices for disabling and enabling indexes.
It is important to use these features cautiously, as they can have a significant impact on the performance of the queries that rely on the indexes.